Proof of Asset Dashboard
The Chronicle Proof of Asset Dashboard enables users to visualize data verified by Chronicle's Proof of Asset Oracle. It provides insights into key financial metrics associated with verified assets such as Net Asset Value per Share (NAV/S), 7-day average annualized yield, custodian information, and more.
This dashboard is designed to enhance transparency and trust in onchain representations of real-world assets by offering a clear visualization of their value and underlying assets.
Learn more about Chronicle's Proof of Asset Dashboard in this video:
How is the Proof of Asset Dashboard different from other RWA Dashboards?
Chronicle provides end-to-end data about a tokenized fund by connecting directly to the custodian. Users can verify attestation signatures in the browser via the Verify button.
The signature process has two layers:
1. Publishing to IPFS: Data is fetched from the custodian, formatted, and published to IPFS. The IPFS URL is content-based, so any change in the data alters the URL, helping detect potential manipulation.
Data is pulled from the IPFS document stored which can be accessed using a unique CID (Content Identifier). The CID itself is based on a hash of the document, meaning that if the content changes at all (even a single byte), the CID will change. This acts like a built-in verification layer, if the CID matches, the content matches as well. There is also a ?checksum= parameter in the URL, which is a keccak256 hash of the document’s actual contents expressed as a JSON string.
e.g.: ipfs://QmPv8UFfZAk7CiNLAW16ZBic741aWtFMXjbU3KkxrRR8Ma?checksum=0xd3e407f7243336f4ba79027b439bcf6a534ffed8fb4d1cc3acfe014d28127774
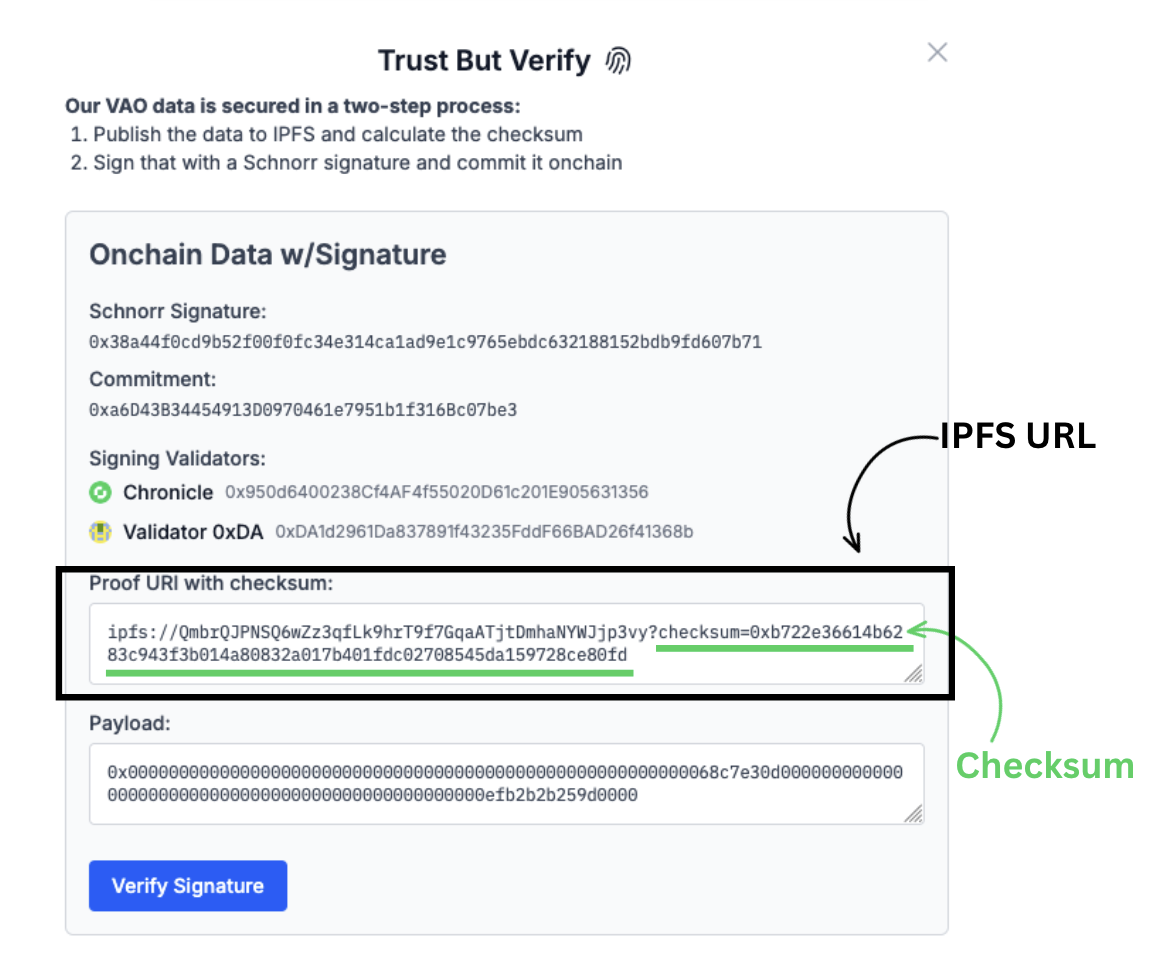
The CID ensures the data hasn’t been tampered with, as it won’t resolve if the content changes.
2. Checksum verification: A checksum of the data is added and verified onchain via a verifier contract.
The checksum proves that the content of the document has remained the same since its initial publication.
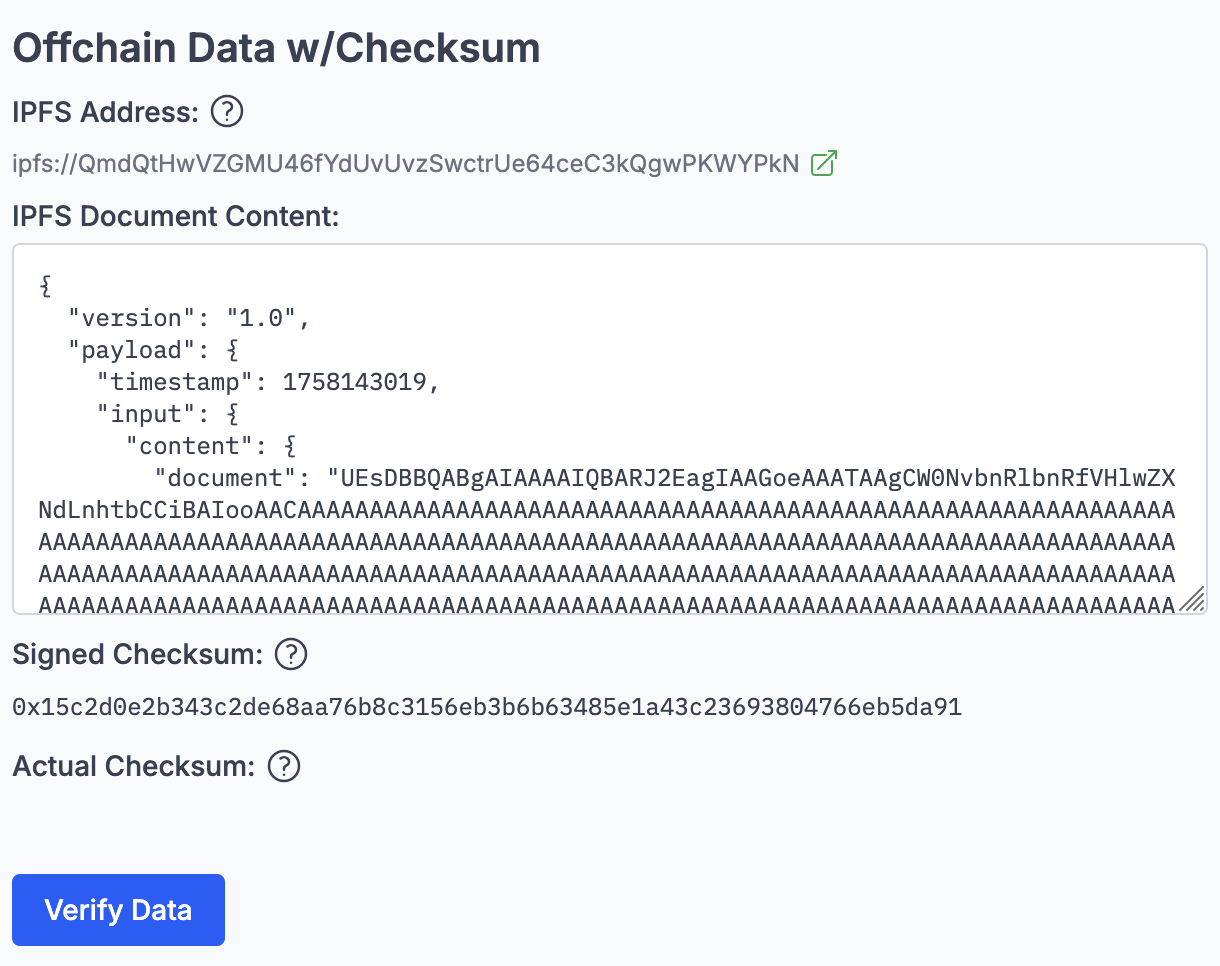
Verification Flow
When someone downloads the document from the link:
- They can calculate the hash of the content themselves.
- Then they compare it to the
?checksum=in the URL (which was previously published). - If it matches, it proves that the document is the same one that was originally published
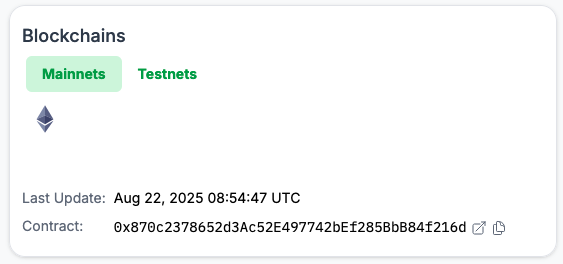
Blockchains
This module shows the contract addresses of all oracles deployed for the asset. These contracts are responsible for reporting the price of the asset on the chain where they are deployed.
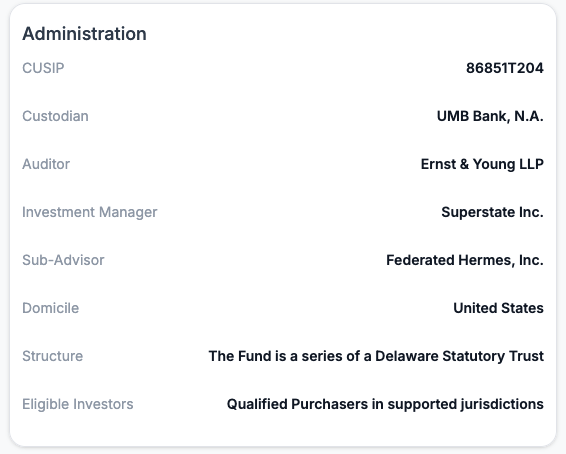
Administration
The administration module outlines the asset's traditional finance infrastructure. It includes identifiers like the CUSIP, details of the asset's custodial bank, identifies the independent auditor/s ensuring reporting accuracy. It will also identify the asset's investment manager and any sub-advisors handling portfolio decisions and specify the fund’s legal structure, domicile, and eligibility requirements for investors.
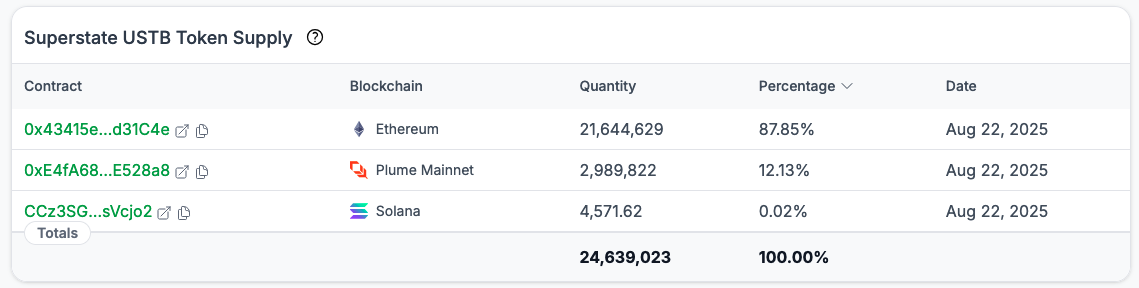
Token supply
Contains the addresses for all ERC20 token contracts for the asset, which chains they live on, and how many tokens have been minted by each contract.
Verifying the Token Supply
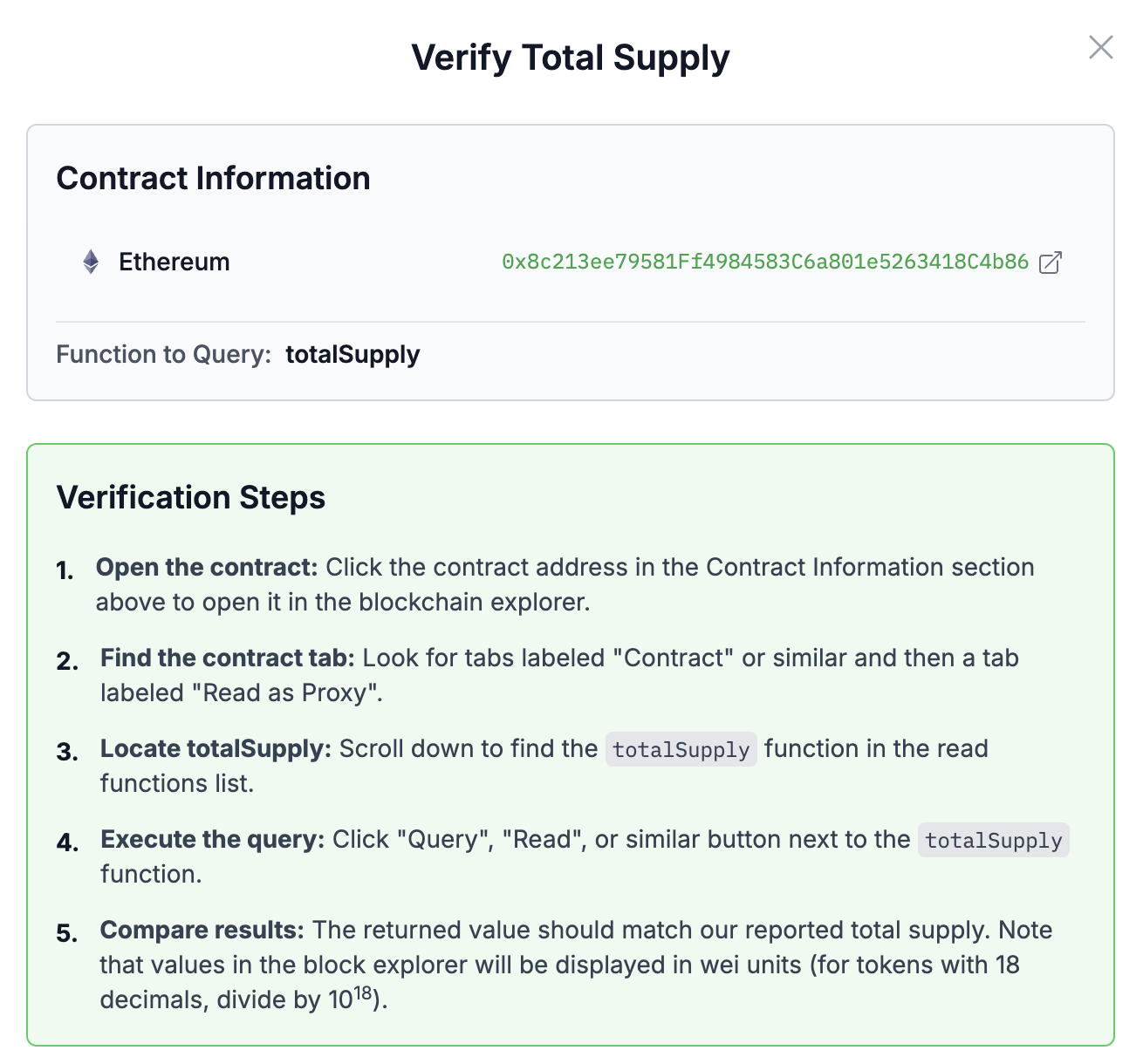
The Verify button enables users to check the value of the underlying assets onchain. By searching for the contract on a blockchain explorer, navigating to the Read as Proxy section, and locating the totalSupply function, users can run a query to view the issued token supply. The result should match the reported total supply, keeping in mind that the number may appear in wei (requiring division by 10¹⁸ for tokens with 18 decimals).
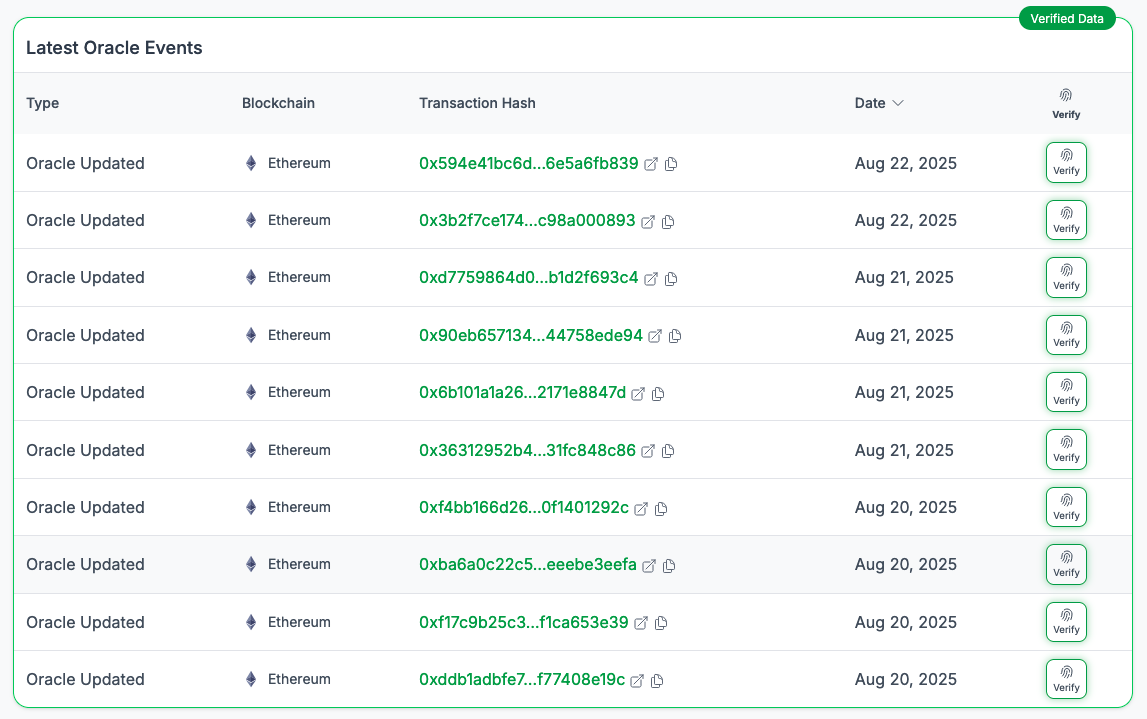
Latest Oracle Events
The latest oracle events module displays all blockchain transactions that have included any of the asset's oracle contracts. These are primarily price updates but other transactions may appear here such as the whitelisting of new validators.
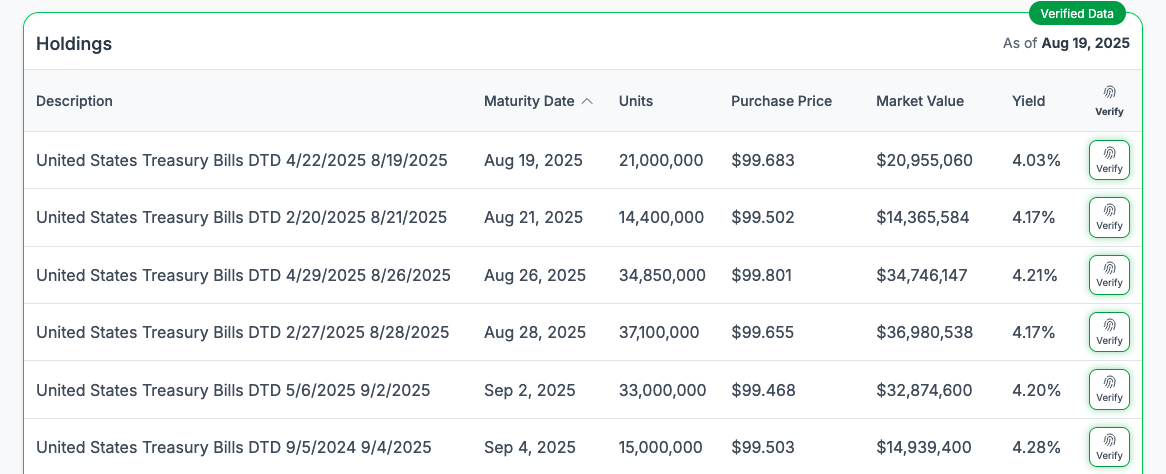
Holdings
This section displays all underlying real-world asset holdings that contribute to the asset’s value, AUM and NAV. It allows users to see the precise composition of the fund. Information may include each asset’s value, purchase price, and, where applicable (such as for bonds or warrants), the expiry date.
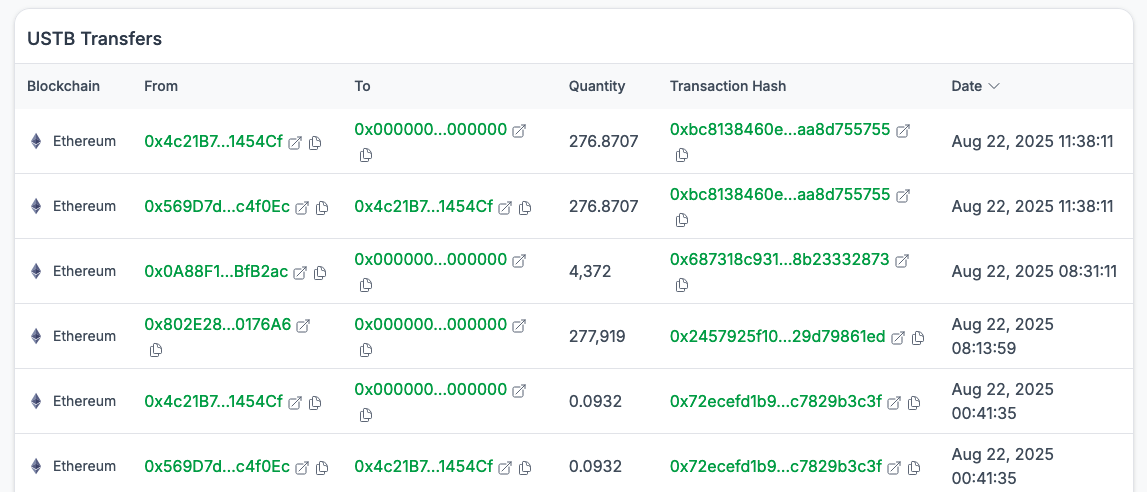
Transfers
This section shows all ERC-20 token transfers related to the fund’s tokenized representation.
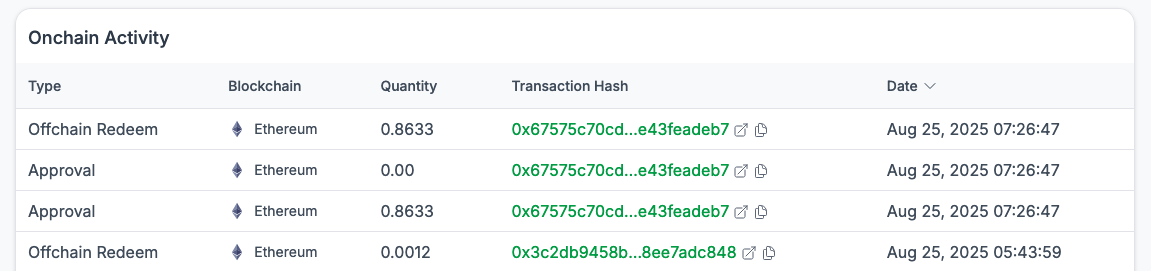
Onchain Activity
The onchain activity section provides a transparent view of all onchain events associated with the fund’s tokenized representation. These may correspond to key events such as issuance, purchases, or deposits into DeFi protocols. Each entry includes details such as:
- Type – The kind of activity, such as Offchain Redeem (redeeming tokenized assets against underlying holdings) or Approval (granting smart contract permissions).
- Blockchain – The network where the transaction occurred (e.g.: Ethereum, Plume Mainnet).
- Quantity – The amount of tokens involved in the transaction.
- Transaction Hash – A unique identifier that links to the onchain transaction for verification.
- Date – The timestamp of when the activity occurred.
These records enable users to trace and verify all relevant token activity directly onchain, ensuring transparency across networks.